AI 101: Is OpenAI’s o3 AGI?
How the new model marks a significant breakthrough in the race to achieve AGI
Welcome to another edition of AI 101, where every Wednesday we bring you the biggest AI update of the week.
This Week’s Update: OpenAI Launches o3, Its Most Powerful Model Yet
On December 20th, OpenAI concluded its “12 days of OpenAI” promotional event with the announcement of o3, its newest and most powerful generative AI model. Through its “chain-of-thought” reasoning and other undisclosed methods, o3 has come the closest to “artificial general intelligence” (AGI) of any AI model to date.
AGI is a hotly debated term, though its definition usually includes the ability to acquire skills and generalize across a wide range of tasks. AI systems like ChatGPT learn through extensive training on significant amounts of human data. While this makes AI good at common tasks, models typically struggle with uncommon ones. Addressing this discrepancy, the ARC-AGI benchmark measures a model’s ability to learn new skills on the fly by testing it on unknown tasks.
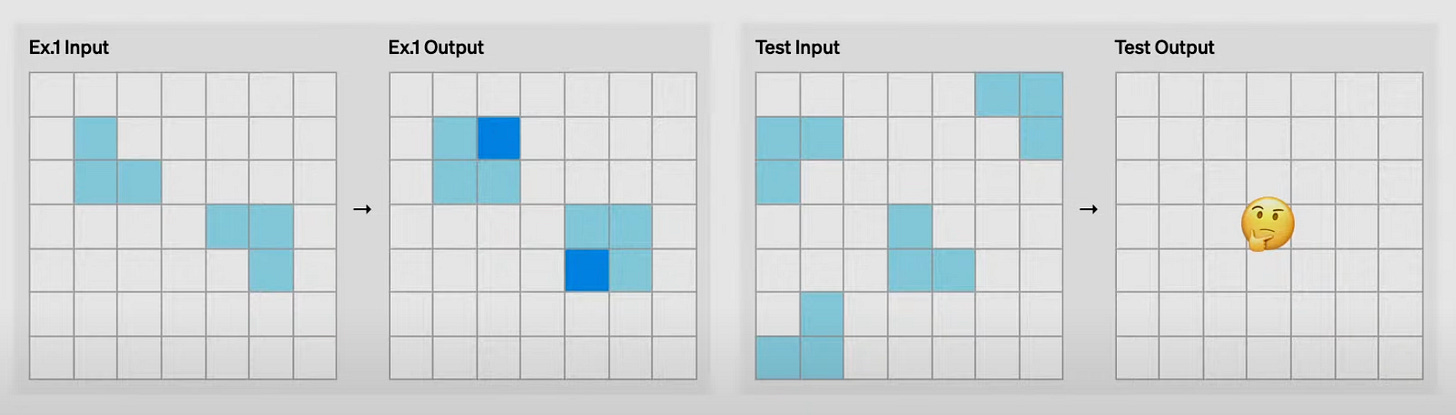
Take the example below. Most humans could solve this puzzle easily, but AI struggles to do so.
Until now, AI has never been able to solve the following problem.
o3 can solve the problems above and has shattered previous ARC-AGI benchmark scores. It took leading generative models five years to improve from 0% to 5% on the ARC-AGI-1 test. On 100 tasks never seen by the model before, the “low-compute” mode of o3 scored a 75.7% and the “high-compute” mode scored an 87.5%.
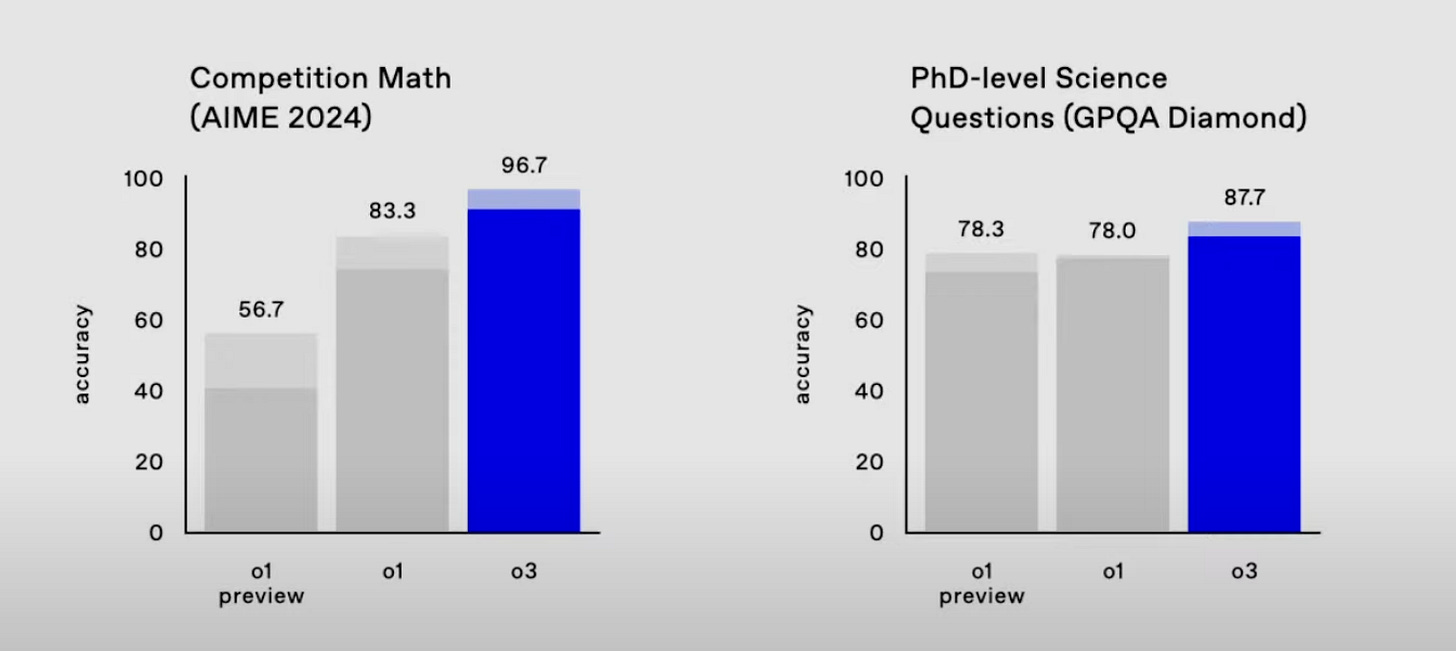
The model also achieved unprecedented performance on standard human benchmarks in software engineering, coding, math, and science. o3 scored 2727 on the competitive coding benchmark, effectively making it the 175th best competitive coder in the world according to the Codeforces leaderboard.
However, there are significant caveats. Currently, o3 is extremely costly to run: on the ARC-AGI evaluation, the low-compute mode cost $20 per task while the high-compute exceeded $1000 per task. For comparison, o1 in high-compute mode scored 32% on the test at less than $10 per task. The model is also only accessible to safety researchers who must apply for access.
Why This Is Important
o3 is the most significant breakthrough in generative AI in the last few years. Its significant improvements have alleviated fears that hitting “the data wall”—when all public training data is exhausted—would stifle AI’s advancement. o3’s impressive benchmark scores may also indicate that widespread task automation using AI is closer than once thought.
However, whether the model has truly achieved AGI is debatable. ARC-AGI-1 tests models on a public evaluation set of 400 tasks, and high scores are verified with a semi-private set of 100 tasks. Crucially, the o3 model provided by OpenAI was trained on 75% of the public data set, and the model still fails some very easy tasks. ARC-AGI-2 is currently being developed and will likely prove more challenging for o3 but just as easy for humans. Despite these limitations, o3’s substantial advancements may indicate that full AGI is just around the corner.
Quick Hits:
OpenAI revealed a more effective alignment technique for its o-series models called “deliberative alignment.” The approach is the first to directly teach the model the text of its safety policies and train it to deliberate over these policies.
OpenAI now offers free ChatGPT access via phone at 1-800-CHATGPT with a 15-minute monthly limit per U.S. phone number and global messaging on WhatsApp.
Italy’s privacy regulator fined OpenAI $15.5 million over its use of personal data to train its ChatGPT models.